A pioneering research has produced the most comprehensive map of a mammalian brain ever recorded.
The 3D diagrams showcase over two miles of neural connections, nearly 100,000 neurons, and approximately 500 million synaptic junctions—all within a fragment of mouse brain not larger than a speck of sand.
Dr. Clay Reid from the Allen Institute for Brain Science in Seattle stated, "Within this minuscule particle lies an intricate network of connections, governed by principles we are just starting to unravel."
The specimen originates from an external section of the brain called the cortex, a zone that plays a role in vision. Times reports.
Dr Forrest Collman, of the same Institute, said: 'By studying how the cortex functions in the mouse brain, we can generate better ideas and hypotheses about how our own brains work.'
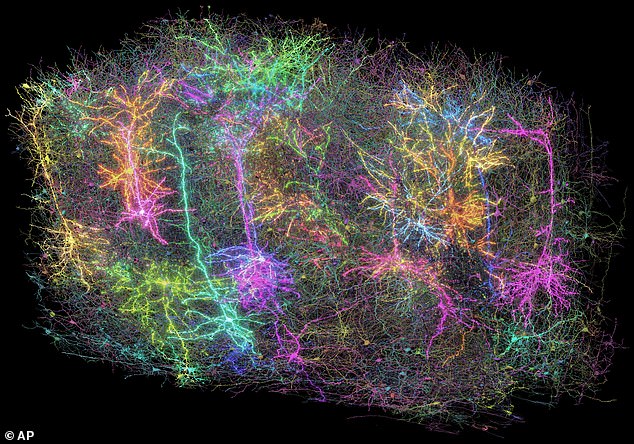
His group thinks that having the ability to chart and examine the brain’s internal connections at this scale could pave new avenues for understanding and addressing neurological disorders like Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's and autism.
He described it as the 'Google Maps for the brain', which doesn't just show major motorways but every small street, house and room inside that house.
Similar to how individuals utilize Google Maps to determine the optimal path from location A to location B, or simply to verify if such a route is possible, this comprehensive neural map enables researchers to identify whether two neurons are interconnected and precisely pinpoint where these connections take place.
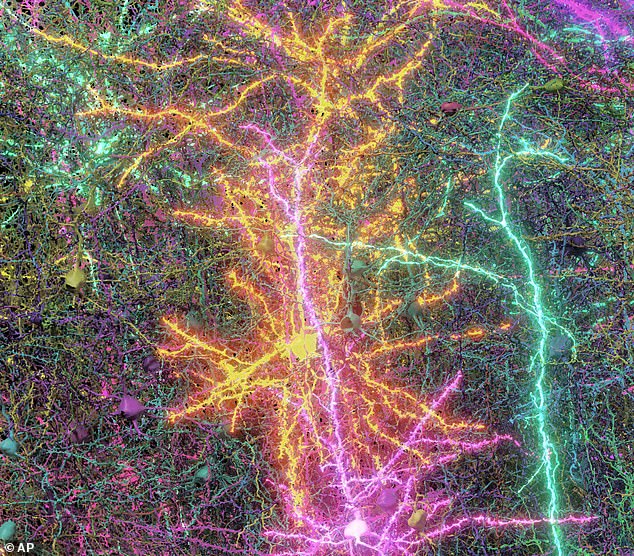

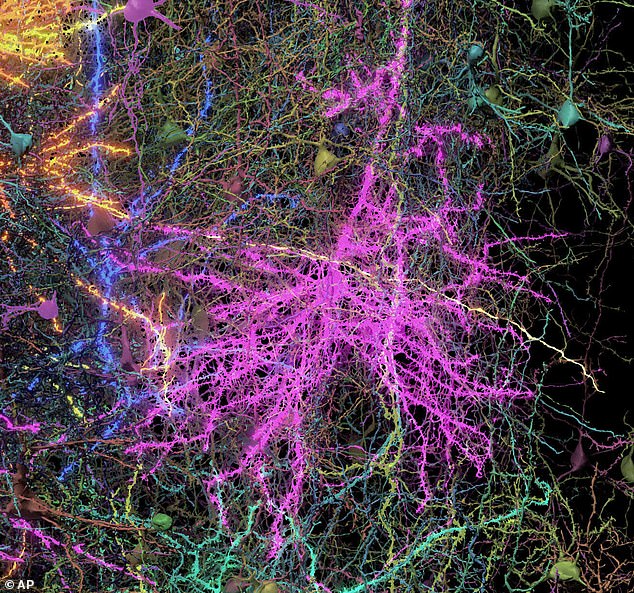
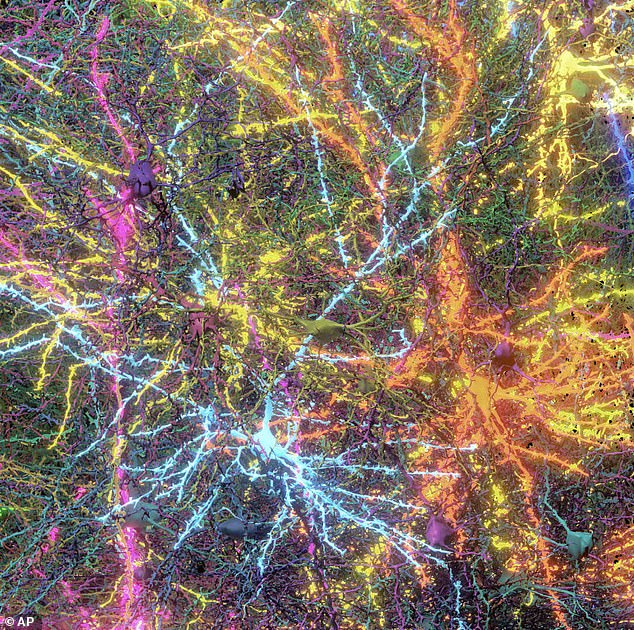
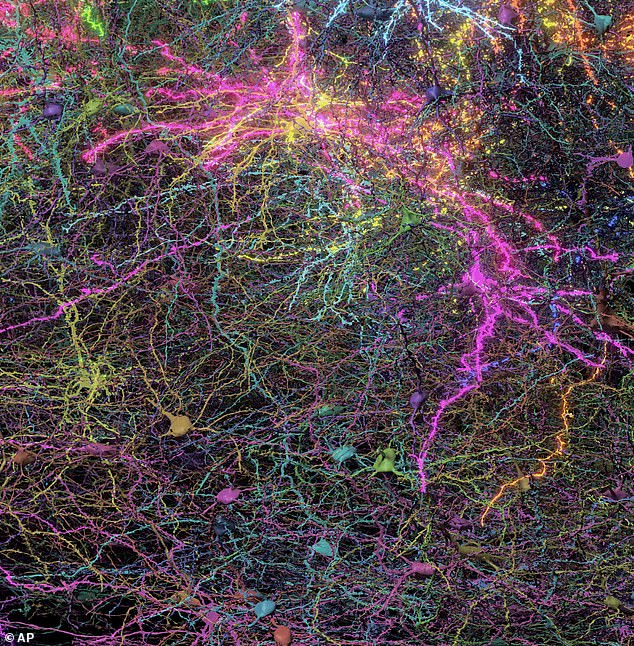
What made this research particularly intriguing was that the mice needed their brain activity documented as they viewed YouTube videos. This enabled researchers to observe the interactions between various clusters of neurons.
Following this, they cut the tissue into 25,000 slices, with each slice being merely 1/400th the thickness of a human hair, before examining them through powerful electron microscopes.
The images were combined to generate a 3D model with the help of artificial intelligence. The final result not only depicts the structure but also illustrates which brain cells interact and the manner in which they do so.
Nuno Macarico da Costa from the Allen Institute remarked that one of the outcomes of their project reveals "just how extraordinarily beautiful the brain truly is."
Simply observing these neurons allows one to grasp their complexity and size, instilling an overwhelming sense of wonder towards the brain.
Read more




